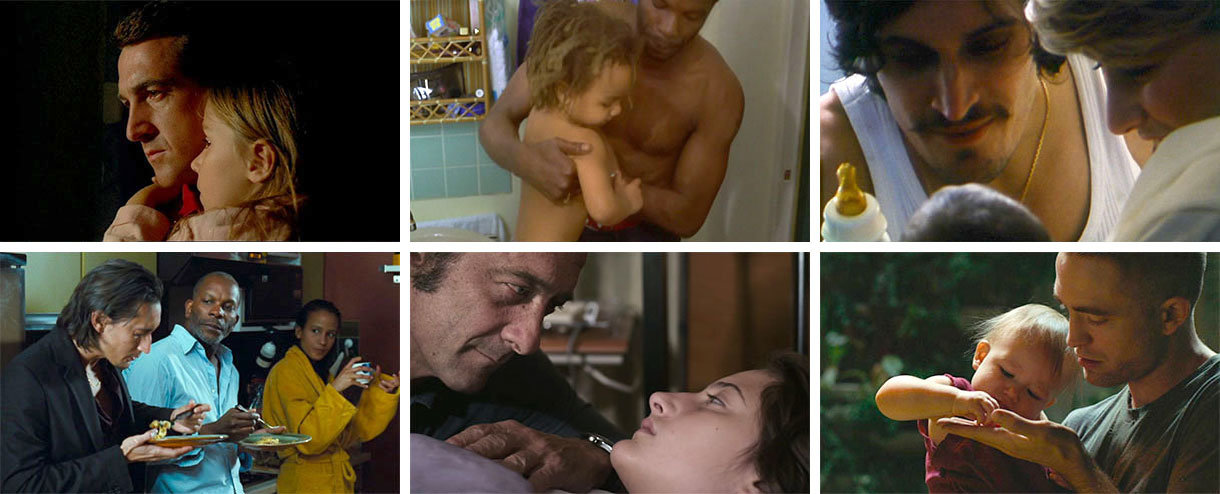
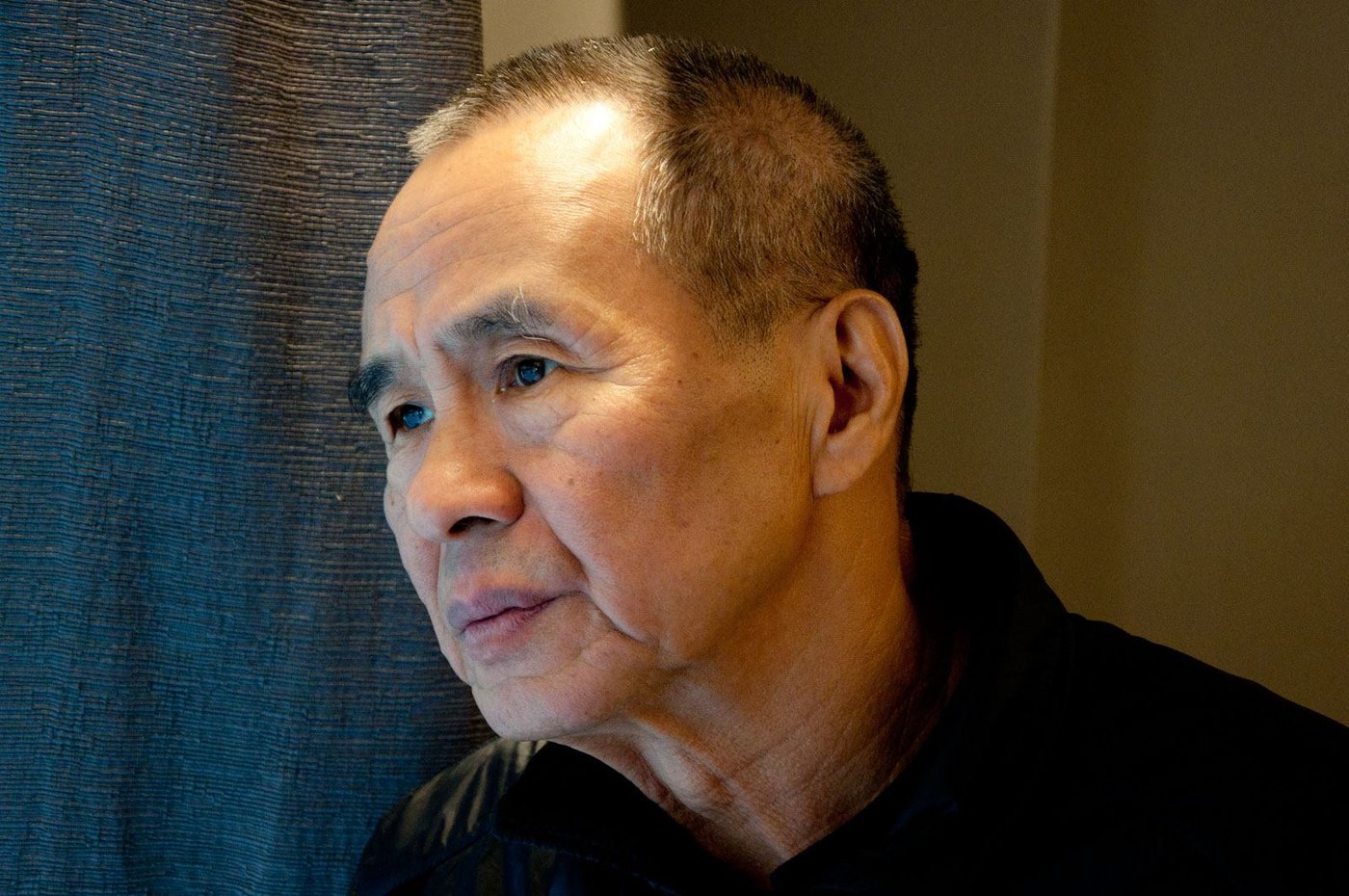
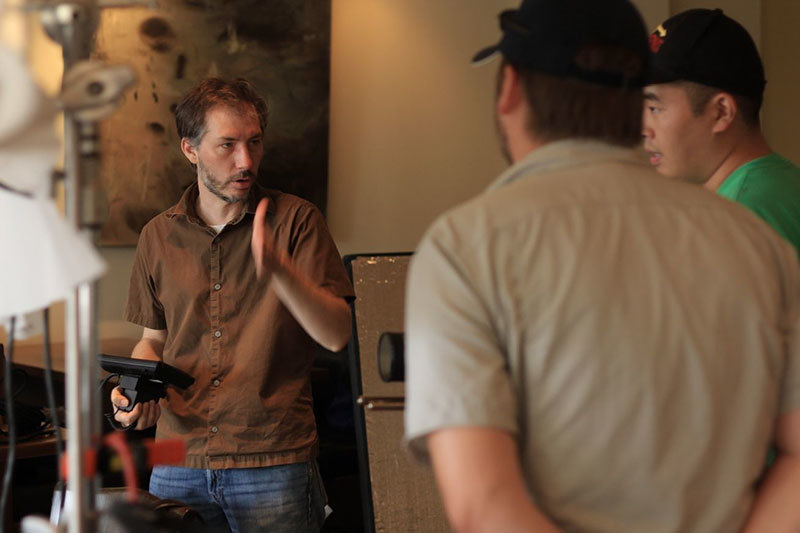
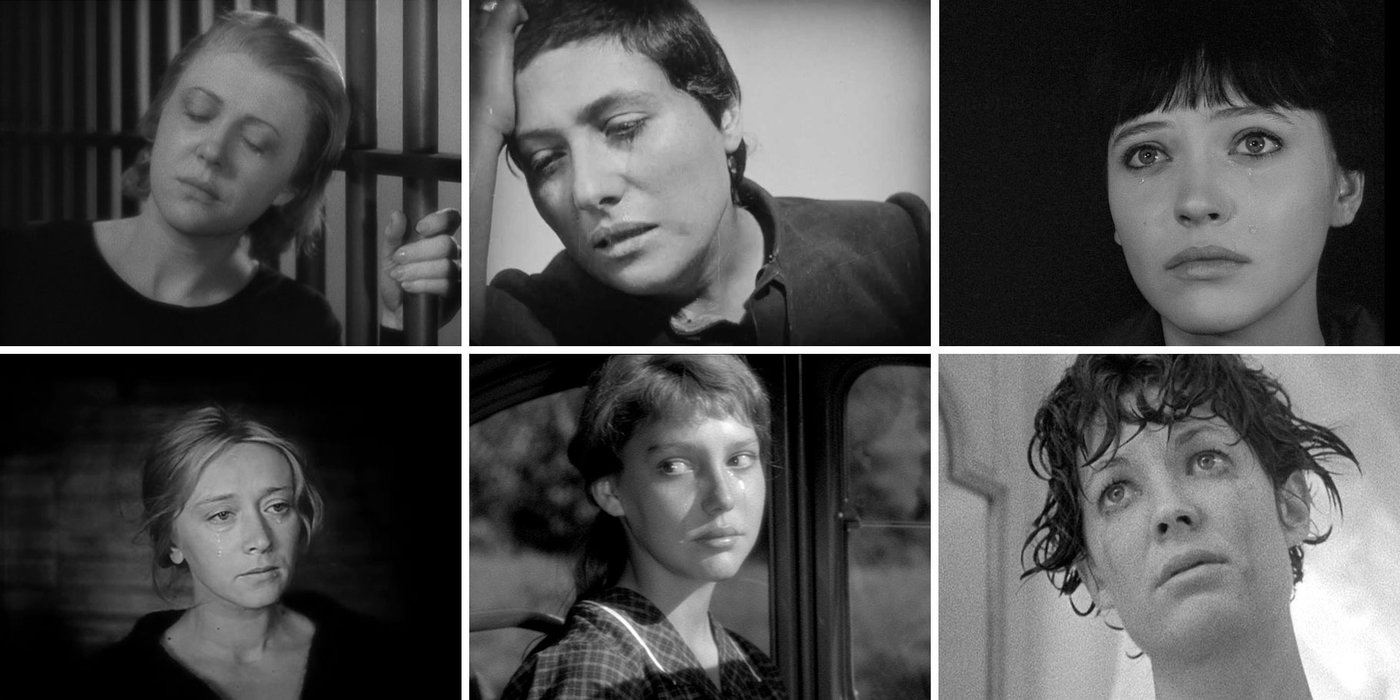
There’s no exact equivalent in film history for Philippe Garrel’s “family cinema,” as he calls it here. To immerse oneself in his work is to watch Garrel and those he loves (parents, partners, children) be transformed by age and experience, while their passions and preoccupations—that particular Garrelian amour fou—persist.
After several decades during which Garrel’s films saw limited distribution and exhibition in North America, he’s now experiencing something of a revival. Over the span of three days at the Toronto International Film Festival I enjoyed an impromptu Garrel family retrospective. In the Cinematheque program, TIFF debuted its recently-commissioned 35mm print of Jacques Rozier’s first film, Adieu Philippine (1962), which features a middle-aged Maurice Garrel in a supporting role. Actua 1 (1968), Philippe Garrel’s long-lost short documentary of the May ’68 protests, screened in the Wavelengths section, also in a new print. And Philippe’s latest feature, In the Shadow of Women, with an appearance by Louis Garrel as disembodied voiceover, had its North American premiere. In the Shadow of Women begins its U.S. theatrical run this week, courtesy of Distrib Films.
It was also at TIFF that I heard rumors Garrel would be making his first trip to the States in more than a decade for the New York Film Festival. Rather than conduct a series of brief interviews, Garrel instead requested a three-hour, wide-ranging discussion. I am grateful for having had the opportunity to join Eric Hynes, Vadim Rizov, and Nicholas Elliot at that table. Garrel spoke at length and with great humor and enthusiasm, noting with a laugh when comments were off the record. It would be impossible to overestimate Nicholas’s skills as a translator.
We agreed as a group to publish the entire interview with only a light edit so as to maintain the flow of the conversation. See also: Part 1 at Filmmaker Magazine and Part 3 at Reverse Shot. The interview was conducted on the morning of October 7, 2015, the day after the NYFF premiere of In the Shadow of Women and soon after news broke of Chantal Akerman’s death.
* * *
Part 1
Edited by Vadim Rizov at Filmmaker Magazine
The interview begins in response to a query from Garrel to Hynes as to whether he’d passed along a message to a filmmaker; then he explained who he was talking about.
Garrel: He was at Cannes, I was showing La cicatrice intérieure. At a crossroads at Cannes, he caught me — I was with Nico — and said “I know who you are.” And I said, “Who are you?” “I’m Jim Jarmusch.”I said, “I don’t want to speak.” And he said, “It’s a pity!” I always remember that scene, that I refused to talk with a young filmmaker from my generation, because I was afraid he’d take my wife!
Hynes: He was a good looking guy in those days.
Garrel: Yeah, exactly. He’s not presentable nowadays?
Hynes: He’s very presentable.
Garrel: His last movie was fantastic. I thought it was a low-budget movie. It’s not.
Hynes: It’s not super low-budget.
Rizov: And he got tax breaks by shooting in Detroit.
Garrel: Like $4 or $5 million. Not a one-million budget.
Hynes: But I think that he often goes to Europe for financing.
Garrel: Ah, that’s why. Because ten years ago, a lot of people said, “[There is] no more money” — during the subprime crisis — “in New York. Everybody has gone to Detroit,” like you said. Nobody wants to — can, not want — put private money into a movie like before, so I thought it must be a low-budget movie. Why the movie is great is because it’s one of the good films in digital. If you look, in general, the photographic artistic level has dropped except for Jarmusch and Blue is the Warmest Color, which is a fantastic film.
Hynes: Is there anything about seeing those films that makes you curious about trying it yourself?
Garrel: I’m like this group of Hollywood directors who went to see Kodak in Manchester and said, “We’re still going to shoot film. Even if our films are distributed on digital, we’re going to shoot on 35mm.” And I was one of the first in Paris to say, “I’m going to stop shooting if there’s no more 35mm.” It’s like what Henri Langlois said — Henri Langlois, who is one of the five major friends of my life. We were friends in the ’70s. He said — at one point people were saying black and white was going to disappear — “It’s impossible. Black and white cannot disappear, because cinema was invented in black and white.”
And it’s true: for ten years it was very difficult to make films in black and white, but then it came back. So now, I think it’s a similar thing. People have said that 35mm is finished, it’s over. I don’t think it’s true because it’s the same thing. Cinema was invented in 35mm. So I think this is just a passage we’re going through, even though distribution has been generalized to be in digital, because it’s easier. But I’m sure I’m right, and I’m like these Hollywood directors who will keep shooting in 35mm. And in France, they’re even now shooting advertisements on 35mm, so it will continue.
Hughes: How do you decide between black and white and color?
Garrel: Many directors are frustrated actors or writers, and some are frustrated painters. Me, when I was a child, I was a painter. I went to a public state school at one point that was at the Louvre. It was called the “Arts Decos’” [the Decorative Arts School], and I was in a specific workshop that was for people under 15. That’s what really brought me to art, this workshop for people under 15. I was very good at pencil drawing, and I was good at gouache, but when I first tried oil painting, I found my painting very bad and I broke it, I destroyed it. That’s when I decided I would make films.
For me, black and white is like a pencil drawing, color is like a gouache, and it’s because of that moment, with that first oil painting — when I was maybe 13 or 14 — I realized it’s very, very, very hard to do oil painting. It’s not like gouache. Mixing colors with oil is much more complicated. If you put a blue and red together, it won’t be a violet like it would be in gouache. It would be a brown. So, I’m scared of color, and I make three black and white films for one color film. Overall, I’ve made four more black and white films than color films.
Hughes: When I think of your films, I think of a close-up of a face against a white background, or a white-washed window. When I saw A Burning Hot Summer a couple of years ago, it was shocking to see Louis’ face against those blue and red walls in the apartment.
Garrel: Yes. There’s also an economic aspect to this. For me, to make a film in color is twice the cost of black and white. That’s not really because of the cost of buying the film or the lab work, that’s about the same today. The reason is that for me to shoot color, I need not only a DP, I also need a costume designer and a set designer. This is something that I learned from Raoul Coutard. Raoul Coutard told me this about Godard and he also told me this regarding Antonioni — where you find emotion in the red, for instance, regarding Antonioni. The thing with color photography is that it’s not only about lights, so you don’t only need a DP, it’s also about the color tones that you use. That’s why you need more money. When you’re shooting color, you need to change the sets, you need to change the walls, you need to change the costumes.
What Coutard explained to me — Coutard, who is alive but he’s no longer shooting, and he’s the greatest French DP — he explained to me that in Godard, and also in Jacques Demy, the range of colors that would be used was decided beforehand. Godard uses the three primary colors: red, yellow, blue, and also green. Antonioni is the same thing: you don’t have pink, violet, etc. I think that’s where you get the special chromatic effect that I find emotional.
Demy is the opposite: you have violet, pink, etc. But if you want to avoid having colors clashing, the way they do in life, you need to make sure you have a harmony of colors, and for that, you have to transform every set, every costume. You need to put paper up on the walls that you’ve made in special workshops.
The reason I’m talking about economics is that if you look at Jealousy and In the Shadow of Women, for example, these are real low-budget films. They’re about a million, a million and a half each, so really low budget. I pay the bottom union rates. It’s very quick, they’re made in 21 days. Another thing about black and white is when I shoot black and white, I don’t use make-up. The women don’t wear make-up, not even their own personal make-up. They’re not allowed. But if I shoot color, immediately I have to have make-up, because otherwise that means the skin will be red. That means more lights, you have to have a make-up person, so you’ve got a heavier, bigger crew.
Another reason I shoot black and white is so that I can make low-budget films, and that’s the condition of my freedom. That’s how I stay free. If I make for one or 1.5 million, I demand, in exchange, total freedom. I get final cut, no one has any right to have any influence on the cut of my film or anything — the distributors, the financiers, they can’t say anything. But I couldn’t request, or be able to get, that kind of freedom, if I wasn’t less expensive than the other directors.
That’s something that I understood from Godard. I understood that Godard was the most avant-garde director of the French New Wave because he was a little less expensive than Truffaut, Chabrol, and the others, and it’s similar to how I am now vis-a-vis Desplechin or Carax. My films cost about half the price of their films. I understood that about Godard, that he was more avant-garde through being less expensive. And it wasn’t by exploiting his crews, it was about being faster. He shot in less time, he edited in less time — that’s the condition of my freedom, that’s how I can keep my freedom, and it’s something that’s very rare in the US today.
Hynes: This is related to something you and I talked about last year, about working with single takes for the most part, and there being a practical reason for that. But then there’s an actual effect of that too. Hearing you talk about all the reasons you work in black and white — financially, logistically, and in terms of your own control — there’s also an effect from that. So you make a practical choice about make-up, and yet seeing your actors on screen in that manner has an effect on us as an audience in terms of how we approach them as people. How do you see the value in that as an effect?
Garrel: When I made my first films — Marie pour mémoire, Les hautes solitudes, L’enfant secret… I’m talking about the films that I produced myself, which here were probably only seen by cinephiles. I made these films with no money at all. That’s how I’m different from the New Wave, because I made films like a painter painting. I took some money that I got from patrons to buy paint and canvas, what painters would do. Now, the New Wave, they made inexpensive films, but industrially they weren’t working like painters. So that’s a difference that I have from the New Wave. I was my own producer for 15 years, and I don’t mean a painter with an office.
What I would do is, I found this idea of asking for the leftover, unexposed film on a roll that was taken out. At that time, when stars acted, as soon as the star had been shot, they would change the roll of film, because they were afraid that the roll would run out if the star was doing something else. So I invented this idea of making features by going around and asking people to give me their leftover, unexposed film. There was so little film, therefore, to shoot, that I couldn’t shoot two takes, it was impossible. So all my films were made in this way. Then in 1983, when I started working with producers, I kept this one-take method. And, in a sense, it’s a lucky accident, a lucky coincidence, because now, if I hadn’t done that, the producers could have forced me to shoot digital.
My first films were shot in 35mm using this method, and when people switched to digital, the argument was that digital is so much less expensive to shoot. So if I didn’t have the one-take method, I could have lost that argument. Now, I make a film with maybe five hours of exposed film. It’s very different from Abdetallif Kechiche, who for Blue is the Warmest Color shot 600 hours. Jealousy, I had five hours of rushes. In the Shadow of Women, four hours of rushes. That’s a huge difference from digital, and, in my case, it’s a method that I’ve had from the beginning.
Hynes: But there’s substance in what the artwork is too.
Garrel: There’s no doubt — unquestionably, this one-shot method leads to a specific genre of film. As I’m the son of an actor who died four years ago now, I’m very, very sensitive to the question of good acting. I work like the theater does. I rehearse long before the shoot, let’s say about 25 days. I rehearse with the actors, and that’s where I do all the directing, in rehearsal. Once we’re on set, I do only one take, and that one take works because of everything that I’ve done before. If I used the traditional method of cinema-making — coming in in the morning and starting to direct the actors at that point — it would be extremely, extremely difficult. It’s thanks to the fact that I added the theater rehearsal before the shoot that we can do this.
And to be specific about it, it’s actually more than theater, because what we do is we work for 25 Saturdays. That’s nearly a year, let’s say about eight months, if you don’t work on holiday, and that allows the role to mature in the actors’ minds [and] the actors to act together. A lot of times now there’s this absurd risk that actors meet on the set for the first time and have never acted before. If only for the chemistry, as they say here, it’s so important for them to be together. So, what I have the opportunity of doing, starting with the casting in these rehearsals, is to match the actors together, to see different people together and see how it works. That’s how my method has evolved.
Many, many French films — not as many American films, but still some — are simply bad because there’s no chemistry between the actors. Directors see an actor, they see an actress separately, they say they’re great, and it’s like they’re putting two photos together. But it doesn’t mean that they can act together, it doesn’t mean that they’ll have chemistry. Hollywood knows that, I think. In France, you can’t test stars together. If you want a star, you deal with the star separately. You can’t test them together. I’m told that in Hollywood, they have readings with stars and actors together so you can see how they go together. You see films where actors may be very good, but organically, they’re not meant to play together; they don’t play together.
My second career is as an acting career. I spent eight years teaching at the Conservatoire in Paris, the national school, also two years at the National Theater School in Strasbourg. When my films don’t make enough money for me to make a living, I sign up to teach acting. It’s there that I saw this business about chemistry — that though actors may have the talent, they don’t fit together. That’s something that you have you to look at in casting. Apart from the Actors’ Studio, in cinema we’re very, very primitive about this question of the association of actors.
Rizov: One of the things I associate with your films is a shot of a face or a whole body in the moment before the actual dialogue and argument of the scene starts. These can go on for a long time. I was watching Liberté, la nuit last night and saw that some of the reaction shots of Emmanuelle Riva are much longer than you let them go on now. This also relates to your work in the ’70s, such Le berceau de cristal, which is a lot of portraiture, which relates to your interest in the screen test. Could you talk a little bit about how long you allow them to get to this point, whether it’s up to them to decide when to enter the dialogue, and how you’ve changed your compression of these moments?
Garrel: Like the New Wave, what I liked best when I went to the Cinematheque was the silent films. For instance, I think that Sunrise by Murnau is one of the greatest films ever made. My three top films are Godard’s My Life to Live, Bergman’s Monika, Munrau’s Sunrise. Why? Because of the faces, the silent shots of faces. Now, when I wrote scripts by myself in the period you’re referring to, the dialogue was very, very short. That’s because I’m a paranoid type. Paranoid types don’t talk very much. It’s like Warhol. I think it’s very useful in art to be paranoid or schizoid. The most paranoid person I ever met, the most paranoid artist, was Warhol. I met him through Nico. He never talked. You would see him standing there all pale in the Factory, never talking, and he made these long, hours-long silent films with no talking. To me, that’s the work of a paranoid man, and I’m paranoid too.
So at the time of Liberté, la nuit, the entire dialogue of my film was three or four pages long. Once I started with co-scriptwriters — this started with Marc Cholodenko, who is also a novelist. This started with Emergency Kisses. He’s more of a schizoid, so my cinema started to talk. There were pages and pages of dialogue. My original thing, though, comes from who I am, and the silent films that Henri Langlois showed me. At the time, the silent directors that people really liked were Murnau, Fritz Lang and — now he’s a little bit out of fashion, young people don’t know him so well — but I loved Erich von Stroheim. These films of von Stroheim’s, you would see them in a kind of half-waking state. It was like a dream, these films were like opium to me. And I think that left a trace on me, aside from my personality, which is to not talk very much, at least not in art, not to declare. This combination of the paranoid and the silent films is what had an impact. Now, today, things have really changed because I work with co-screenwriters.
Hughes: My favorite moment in In the Shadow of Women is when Pierre and Elizabeth are sitting on the bed together. I think he’s fixing a coffee maker, and he hurts her feelings, and she leans forward. She’s so delightful before he makes the hurtful comment, she’s just staring at him and admiring him, and then when he hurts her she leans forward, toward the camera, and makes this gesture with her hand. It’s really lovely, and I’m wondering — you talked about 25 Saturdays of rehearsals, and I’m wondering what the scene looked like at the beginning of those 25 days versus the one when the camera’s finally rolling and you get that one take. Where does that gesture come from? How are those choices made?
Garrel: All the young people in my films since Savage Innocence, which is 2001, have come from the Conservatoire, the national conservatory of acting Paris where I teach, like for example Lena Paugam, who you’re talking about. In my work as a professor with an acting class, it’s not at all a magisterial lesson. It’s a workshop class. I have a camera man, I have a sound person, I have a small camera, and I get the actors to do scenes in front of the camera. My work is to deblock the actor, to free the actor, to give him the freedom that’s been taken away from him by being filmed. Because being filmed paralyzes him, my job is to remove that paralysis.
So that for example, for that gesture, my responsibility is simply to free the actress. She invents it, she makes the gesture in that moment that you’re referring to where he’s hurt her feelings and she’s repulsed and slightly traumatized. My only responsibility for the gesture is to free her, to be free on the set. Now, some good directors will push the actor. They’re like, “Let me show you what to do,” and then the actor imitates the director. I stay behind the camera. I don’t ever get in front of the camera, I don’t show them what to do, I don’t say what to do, I free them. Now, that takes a very long time, which is why it’s useful to have these many rehearsal days that I use. All my recent films — Savage Innocence, Regular Lovers, Jealousy, etc. — have actors from the Conservatoire, either people from my own classroom or, because I’m a titular professor there, people who I see at the graduation exercises in the new classes.
So the level of acting is reached by the level of freedom; the actor has to be himself and to act only like he would. And that’s what’s touching about it. In Regular Lovers, for instance, the May ’68 riot scenes, all of those people — 45 actors — come from the Conservatoire. So what you have behind that is six years of work in my class. School nourishes the set for me. And my son has been my student too in class, so he knows very well what the other students have done. It’s not like he is only my son, because he’s just a student like the others.
Part 2
Edited by Darren Hughes at Mubi’s The Notebook
HYNES: I’d love to know for you the relationship between teaching and directing. Is there a real overlap in those two jobs? And more specifically for this film, did your directing start well before the shoot? Do you think of it in those terms? Or are there points when you feel you’re primarily teaching? How do those two jobs evolve over the course of a project?
GARREL: It’s the same thing. It’s like playing tennis. The tennis match is the shoot, the training is the classroom. The only difference, I would say, is that when I’m on the set, I only talk to the actors separately, secretly. I don’t let the others hear. Whereas, when we’re in the classroom, I do let everyone hear so that they can learn from it. That’s the only practical difference.
When I chose what my profession would be, what my craft would be, which was after this business of the failed oil painting, I remember I was waiting at the bus stop and I saw a poster of a Marcel Carné film that was playing at the time starring Jean Gabin and Michèle Morgan [Port of Shadows (Le quai des brumes, 1938)], and I thought to myself, “I’m not able to act, but I would be able to tell actors how to act well, because I’m the son of an actor.” So, that at first is what I realized I could do. Nine-tenths of directing is directing actors. In school, they put way too much emphasis on camera placement and so on, whereas really that’s just one-tenth of directing a film.
When I had kids, and I wasn’t as well known then, I was able to make a living by becoming an acting teacher. By thinking that you know something, you’re able to convince other people that you know it, and you become respected for it. It’s kind of like working with a psychoanalyst—by believing that the psychoanalyst is a wise man, you in fact heal yourself. It’s the same with an actor. I can say for myself that I’m a conductor, except that I’m a conductor who doesn’t know how to play any of the instruments.
HYNES: You talk about your father being an actor, and you felt emboldened in terms of offering that to others, but if I’m not mistaken you father was ambivalent about being an actor. You seem less ambivalent about being an actor and a director than he was. There’s a legacy of acting that you’ve inherited, but you’ve inherited it without the reluctance.
GARREL: It’s true that my father was like a hidden actor. He was mostly a theater actor, not a film actor, and the reason for this was that during the war he landed—he invaded in Provence and in Italy and he had killed people. This was a huge problem for him because my father was a humanist [yet] during the war he had been forced to do this. He had signed up with the North African Free French troops and he landed, like Samuel Fuller and others. He used to say to me, “There are no murders in war, Philippe,” but still, because he killed, it was very hard for him. At the end of his life, he explained to me that he had hidden himself away in a small profession, the small profession of being a theater actor.
He also was a puppetmaker and puppeteer first. When I was born, that’s what he was doing—acting with Jean Dasté and Gaston Baty. Gaston Baty belonged to the so-called “Cartel,” which was Baty, [Jacques] Copeau, [Charles] Dullin, and [Louis] Jouvet. My father was a student of Dullin, and my method comes from Dullin. Dullin is someone you might have seen in a few films around the second world war, but he was primarily a theater actor. That’s where most of his leading roles were. So when I was around six or eight I would go and sit alone with adults at night in the theater and watch my father on stage.
But it’s true he was ambivalent about it. He considered it a small profession. In a way, that’s something that I inherited from him.
RIZOV: I want to follow up on that a little bit. You talk about the work of unblocking the actor. When you were working with your father—especially regarding his experience in Algeria, which is addressed in Liberté, la nuit—did you have to unblock him in relation to his own experience to then relive it on screen?
GARREL: Just once. Other than that, I never directed him. He did it all alone. And on the contrary it was me who learned from him.
But for the last film he made with me, Un été brûlant, which was actually the last film he ever shot, I gave him a supporting role—he was too old to play a leading role—and he was acting with his grandson, Louis Garrel, and he was telling an incident from the war. For the first time I had seen with him, it was reality for him. It wasn’t improvising, it was reality. He started acting not just for Louis, he was acting for the crew as well, as if it were a confession. The crew included great, experienced members like Willy Kurant, the D.P., and he was talking to all of them. So it was the only time in my career that I decided to do a second take with him. I told him, “No, you have to talk just to Louis.” It was the only time I directed him, and it was for his last role. I think it was because he was so old that for him there was no difference between acting and being.
HUGHES: I’m deeply moved by that scene with your father, partly because as a cinephile I have a unique relationship with your family. A few weeks ago in Toronto, for example, I saw the new restored print of Jacques Rozier’s Adieu Philippine (1962), in which we see your father in his late-30s. You’ve been working with your family for several decades now. Does that still satisfy your curiosity and bring you pleasure as a filmmaker?
GARREL: At the moment I’m rehearsing a film with my daughter, Louis’s sister [Esther Garrel], because my family is kind of like the circus. Everyone is in the theater or in film. So right now I’m rehearsing a film with my daughter who’s 23, an actress from the Conservatoire who I found in the recent graduating class and who’s 20, and one of my father’s best friends who’s an actor. It’s very, very important for me that art is grafted onto real, intimate life because a film is a piece of your life. Sometimes it takes a year, sometimes three years. I think it would be hard for me to maintain professional—even emotional—ties with people in cinema if I didn’t have these people from my family around me.
Sternberg had done it before, but what really interested me in the New Wave was that it was a couples’ cinema, it was a lovers’ cinema. Antonioni did it, too. What I think I invented, with my situation, was a family cinema. It’s very important for me that film remain meaningful, that it does not remain outside of the subconscious. Once the subconscious is expressed on the set—and I think this is very important—the film becomes more expressive.
At the end of his two books on acting, Stanislavsky comes to the conclusion that one should leave room for the expression of the subconscious. If you can let the subconscious be expressed in the making of the film, then when the viewer sees the film he will have something of his own subconscious emerge. Not through identification. He’ll think of people he loves, for instance. He’ll think of something that is emotionally moving to him. If my subconscious surfaces in the film and comes through, he will be touched because his subconscious will emerge. In this way, cinema heals.
I look for emotion in truth. I don’t go searching for emotion like some filmmakers do. I think it’s more successful to go looking for emotion through truth because that way the viewer can come to his truth.
RIZOV: In terms of your work with your son, his relative lack of expression is something that’s been discussed a lot. As an example, I’d like to ask about one of my favorite of your scenes that everybody likes, the “This Time Tomorrow” scene in Regular Lovers. Everyone is dancing around him and you cut to him in the middle of it. He’s very unmoved, in opposition to the spirit of the room. How do you develop that characteristic as you direct?
GARREL: In that particular scene, it was a choreographer who teaches at the Conservatoire. At the Conservatoire, they also have dance professors. It’s not just theater and films. Anyways, Caroline Marcadé choreographed the Kinks number.
My set is quite free, and Louis Garrel, in general, is quite inhibited about dancing, so he didn’t want to dance. Since my cinema is free, I said, “Okay, don’t dance. Be a character who doesn’t like to dance.” Then, as we were shooting, I saw that Louis was watching his classmates, because all the others in the scene were people he was at the Conservatoire with for three years. He was watching them, so I told the D.P. to film Louis without telling him. Those are documentary shots that are inserted in the choreography that Caroline Marcadé did.
By the way, I’m working with her again this year, so it’s not just actors that I get from the Conservatoire. I also take professors and use them behind the scenes. For instance, the person who teaches fight choreography at the Conservatoire, I’ve had him act in the films.
My father acted like I never could have imagined. And now Louis Garrel is a much better actor than I am. I try to help him, but most often when he’s stoic like that, these are decisions that he has made among his classmates, people he was in school with for a long time, based on what he can and can’t do.
I try to navigate this family relationship on the set. It can be awkward for people, and I try to avoid that. You have to avoid playing favorites. He and I are obviously very close, but one has to be democratic and not treat him differently. Of course, if we come back to the subconscious, of course I do treat him differently because, for instance, I dream of him more often than I dream of his classmates.
HYNES: You talked earlier about introversion and about how you’re an introvert and there’s an expression of that in terms of lengths of shots and the quietness, to some degree. It’s interesting to me that that’s how you describe yourself. When I spoke to Louis he also talked about your family as being a circus and he likened himself to being the clown in the circus. So, in that sense he seems very different from you. And yet, in your films there is an introversion that comes through at times, and I’m wondering about your relationship with him in terms of him basically being an expression of you in a deep sense. And also, how do you relate to other actors in that sense? Because actors tend to be introverts. As a teacher and a director, how do you work with that dynamic, bringing actors down to a quieter place? Or at other times encouraging their outgoing aspects?
GARREL: When I film Louis Garrel or my actors, even if I’ve written a story based on my own life, it’s really them that I’m filming. When I filmed my son or, back in the day when I filmed my father in films like Liberté, la nuit, I wasn’t asking them to play me. I was really filming them, and it’s been like that since the beginning, even when my films are drawn from my own personal life.
The problem is, for instance, if you’re telling a story that involves sex you can’t talk to your father about sex the way you would with your best friend. What we’re getting to is the problem of incest. In asking my father or my son to be actors, I can’t film my father kissing a woman. I can’t film my son holding a naked woman the way I could with other actors because that would be like looking through the keyhole at my parents or into the children’s room.
It’s Freud who said that the number one taboo for humanity is incest. It’s the most repulsive point. Everything about our evolution as a society is designed to avoid incest. So if I write, for instance, my love story with a woman, and I ask my father or Louis to act in it I don’t ask them to play me. I ask them to play themselves. And not only that, I have to film a purely spiritual love, because otherwise it’s like going and peeking at your parents or going into the kids’ room. You can’t do that.
There’s an inconvenience to that, which is that it makes for a certain kind of story; but there’s an advantage, which is that every time the story has to be of amour fou. It’s not just a little love affair. It can’t be that. It spiritualizes the love while taking away the problem of incest or voyeurism of other family members. So there’s both a limit and a kind of luck in this, which allows a transcendence. Perhaps I haven’t completely answered the question.
HUGHES: You mentioned earlier that you wanted to trigger the subconscious rather than create an identification. When I watched Emergency Kisses for the first time ten years ago, I felt very removed from it. I’m now the same age as you were when you made it. I’m married and have children the same age as Louis in that film. So when I revisited it last week, I identified much more closely with your character, but I was also deeply moved by it because I now understand deep in my bones that the loss of my family would be the great tragedy in my life. I now experience—subconsciously, I suppose—the threat of despair.
GARREL: Well, I think that’s proof of how art is useful. As we see with great filmmakers like Bergman, his films show that he was an artist, but they also show that films can be as useful for healing as a book by Freud.
It’s very important. I deeply believe that art can replace religion, like psychoanalysis can help—not replace but help—medicine. Art can supplant religion as far as belief in life. And that’s what’s sad about Chantal Akerman’s suicide. She was an atheist. My father used to say to me, to deal with suicides, “All young people are suicidal and I was, too.” And he used to say to me, “Suicide is two lines in the newspaper.” And we saw as much.
So, with Chantal it’s a real failure of art, as far as our business is concerned. We can’t get into her private life or the failure of love or any of that. But what we can see politically in her life is the concentration camps, because her mother was in the concentration camps, and we can see that art wasn’t enough for the collective unconscious, as Freud saw the collective unconscious. Not this idea that we have now of a cloud floating above men. Freud saw it as something that’s anchored in our memory and that comes from those who lived before, who came before us, and that makes us act despite ourselves.
As far as friendship and love and so on in art, that’s what art is good for, as the five of us here who agree that art must be defended in this way, because it helps us to live. But even psychoanalysis fails us. We see that with Primo Levi, who had been in the concentration camps and who, like Chantal, killed himself. It’s very, very complicated to heal the psyche through art, through this search for emotion, for reliving things, for bringing things forth from memory and unconscious when we see art. It’s not like we’ve reached the end point with this. On the contrary, we’re at the eve of the importance in our civilization of understanding that art is essential.
RIZOV: It would be hard for me to imagine a film of yours that eliminated political aspects entirely. There is an analytical component in returning to, revisiting, and re-experiencing charged political moments, whether through Maurice’s monologue in Liberté, la nuit about the scars left by the Algerian war, a very short eruption like in Frontier of Dawn when the man at the bar suddenly says, “I’m an anti-Semite,” or in A Burning Hot Summer, when a sidewalk conversation is interrupted by immigrants running from the police. The characters are preoccupied by their lives, while briefly noticing what’s still going on around them.
GARREL: Instinctively, what you’re touching on with all of these scenes is something that I didn’t invent. I didn’t invent this process. Artists have been doing this since the dawn of time. What you’re touching on are dreams that I wrote down upon waking up. Notated dreams. For instance, the murder of the mother in Liberté, la nuit, the arrest of the immigrants in A Burning Hot Summer, these are all dreams.
Now, many artists have done this. They mix imaginary scenes and dreams. But these scenes are not shown as dreams because I’ve also had scenes in my films where you see actual dreams, you see the hero fall asleep and dream. I like to mix those with reality. What I’m interested in is the search for a method, and that’s how you get an avant-garde style—by searching for something new.
In Regular Lovers, for instance, toward the end of the shoot, I had a dream, but instead of writing it down I did something like what Godard would do when he was . . . let’s call it “improvising the mise-en-scene” on the set, where he would make something up and shoot it with without writing it down. So, I had this dream. I called my assistant early in the morning and said, “Go to the store, buy some barbed wire, and come to the set. I’ll tell you why.” We were shooting in the forest, and what I was able to do is I noted the dream directly through the camera. I didn’t write it down. It would be hard for you to remember, but it was the scene where the character takes opium and then he dreams. That was a dream noted on camera. You see a young woman wearing old clothes in a small camp with barbed wire. She’s woken by Louis Garrel, who’s dressed as a young prince. There’s a small flame. He takes her out of the camp.
And that’s how you get to be avant-garde. You try to be the first to make a certain gesture. So, in this case, two or three hours after I’d woken up, I was shooting the dream, noting the dream directly through the camera, while I was still inhabited by it. What I try to do is I take these scenes from dreams, which you’ve instinctually noticed, and I mix them with realist scenes. They’re oneiric scenes by definition, since they’re taken from dreams.
You’ve instinctively put your finger on all of these scenes that were from dreams that were shown as reality!
Part 3
Edited by Eric Hynes at Reverse Shot
HYNES: I don’t usually think of your films in terms of genre. I think of you as coming out of the avant-garde but continually working towards your own vocabulary. But with In the Shadow of Women, you do seem to be in dialogue with comedy. How deliberate were you in bringing in those elements, and how willing were you to go into that area?
GARREL: It’s true what you say, but it was not on purpose. In France, when I saw the audience laughing at the movie, they were laughing at it as if it were a comedy, as if I had told it with humor. It was absolutely not on purpose. I did it without humor. What’s possible, however, is that it’s due to the fact that it’s the first time I’ve worked with Jean-Claude Carrière. When I said to Jean-Claude, “Everyone is laughing in the audience,” Carrière said, “Yeah, Philippe. That’s me!” When Godard decided to make industrial cinema again in 1979, I observed that he worked with his wife, Anne-Marie Miéville, and he worked with Carrière, who as you know had written for Luis Buñuel and worked with Godard on two films, Every Man for Himself and Passion.
The importance is not that I’m avant-garde or a modernist; what’s important is that we say, “It’s cinema,” the way that we can say, “It’s a painting” when we look at a painting. Now, in the modernists that I like—Picasso and Matisse and Max Ernst—you have a figure, sometimes it’s Cubist, it’s de-structured, interpreted, but underneath it you see the classic drawing, you see the construction of the human body. That’s the modernism I like in painting, because the two forms of art I like are cinema and painting. What I’m looking for is how to be modernist in a profound way. But you also have to be classic in a narrative sense. You can’t, with cinema, put the book down and do something else or look at another painting. Only cinema and theater have this thing of imposed time where the viewer must accept to be a prisoner. So, what I wanted to do was be like a painter, to have a classic design underneath (which Picasso could do very well because he was a master draftsman) and on top to deconstruct. I thought Carrière was the ideal person for this because what he had done for Every Man for Himself. What I wanted, in a sense, was a classic script and to do a modern mise-en-scène.
What you see with Godard—and he’s the only one who does this, and this is why he’s so much better than me—is that ten years later, after the movie, you see that he was telling the story. But because of his modern mise-en-scène, the story wasn’t exposed. It appears over time. And in that way he’s like Picasso, or Einstein. Because he’s searching, he’s searching and he finds. For instance, take Nouvelle vague. I had to see it four times to understand the story. People walk out of Godard movies because they say there’s no story, there’s no logic. But there is a story. It’s just exposed differently. For instance, in a classic film you’ll have an actor who says, “I’m the President of the United States.” In a Godard film, you’ll have an actor saying nothing, and you’ll have a voice coming in from somewhere saying, “Mr. President, do you want a glass of water?” That’s his method of exposition. It’s hard to understand. And you need to understand that logic to be moved by the movie. But with time and maybe one sentence in the program, these movies can touch people. Slowly we’re catching up.
If we take the example of Nouvelle vague—which was shown in competition in Cannes because Alain Delon was in it—there were many, many walkouts. Which is what happened to Chantal Akerman’s film, No Home Movie, in Locarno. Godard was used to this kind of treatment. When I took Godard as a master when I was 13 or 14, there were maybe six of us in the screening room to see Alphaville, and at the end there were four. But Chantal wasn’t used to that kind of thing. She filled theaters. So maybe No Home Movie is too modern. Maybe it’s hard to understand. It was the same for Nouvelle vague as it is for No Home Movie. But the difference is that Straub and Godard—they’ve always seen this kind of behavior. They’re used to it. Now when I read the Cannes reviews of Nouvelle vague back at that time, the story they described was wrong. They said it was the story of two brothers and a rich heiress. The critics told a different story than was the movie’s actual story.
When I saw the film a fourth time, I realized that the story was actually of a Machiavellian character who makes people believe that he was killed by this heiress. And then he reappears with another personality pretending to be the first man’s brother. And out of guilt the heiress gives him everything she says to avoid him telling the police about her. At the end, when she nearly drowns in an accident, she realizes who he is. And he saves her. So she says, “But it was you all the time.” And he says yes. And so she says, “But there’s one thing I didn’t understand—why did you save me?” And he says, “Because in the meantime I’ve fallen in love.” Which is very, very moving. But if we don’t understand it, it’s like a math problem.
So back at that time I wrote to Godard, because I write him quite frequently or I go to visit him—and I was right, that was the story. But no one at the time understood it. Except maybe the top student [smiles]. Now everyone understands it. It’s a great story, but instead of exposing it in the Scorsese style, Godard told it in his modern way. It’s a moving story for the 21st century. It’s told in the avant-garde way of Godard. The exposition is too hidden, instead of being really comprehensible. But that’s why Godard is in my eyes the greatest modernist. Why he’s above all the rest. Like Picasso—Picasso who in relation to the Louvre or classic painting in general, he came along and he broke everything. So that he could come after, and that’s what Godard did. After only 80 years of cinema, he came along and he broke the Lumière and Edison things that we were doing, and he invented modernism.
HUGHES: When you talked about seeing Nouvelle vague for the fourth time, you said you came to understand the logic of it, which is an interesting choice of words. All critics and viewers have to wrestle with Godard’s logic, but I’m not sure it’s a word that comes to my mind when watching and writing about your films, which are more about unearthing, in that subconscious sense, the emotions generated by your images. You’ve talked about growing up as the son of an actor, being exposed to art and painting as a young child, but I’m wondering about other sources for your images, beyond dreams. Do you still take direct inspiration from paintings? I’m thinking about the images of feet being held and wrapped and washed, which is a trope in sacred art. Some of your earlier work is almost mythological.
GARREL: The other exercise that I devote myself to, aside from seeing and re-seeing the films of Godard… actually there are two other exercises. One of them is going to the museum. When I was fourteen I lived next to the Louvre, and the Louvre was free once a week. In fact I saw here that on Sundays it’s pay as you wish at the Frick, which I think is a great thing, a democratic thing, to allow poor people to see classic painting. I went to the Louvre every single Sunday. At 25 I counted, and I’d been to the Louvre 147 times. When I shoot, I don’t watch movies—I go to the Louvre. And I look at how they paint things. I don’t look at the dates—I don’t know the history about paintings. I look at the names and I look at the paintings.
The other practice that I’ve undertaken, which I started when I was 25, is that I read Freud. Whenever I had a problem, I read one book by Freud. For instance, if I had an addiction, I read a book by Freud to get over it. And I would say, in the Freudian sense, this is the this of the illness, and I would work through it by reading the book. And then I would not be dependent. Or if a woman had left me and I felt terrible, I would read one Freud book. And no lie, I think I’ve read more than half of Freud. And I did this without undergoing psychoanalysis while making films.
Now, not long ago, I started to experience really visceral jealousy over a woman—a very serious problem. And so for the first time I decided to go to psychoanalysis. And I found an old psychoanalyst who is a disciple of Lacan. And I had a very short psychoanalysis with him—six months to get rid of the jealousy. I didn’t get rid of my other problems, but I did get rid of the jealousy. And so I wrote to this 92-year-old psychoanalyst, “I think I can get by alone.” And because he’s a very wise man, he wrote me, “If you think you can get by alone, you should leap on the opportunity.” So I stopped the psychoanalysis, and I also stopped reading Freud. So here, for instance, in New York, I’ve seen zero films, but I’ve been to the Whitney, I’ve been to the Frick. I’m really, truly interested in that.
So I have classic and modern painting, I have Freud, I have Godard, there’s seeing old films as well. Like recently I discovered some Bergman films that people don’t know very well, from the mid-forties. Like Prison and Music in Darkness. These are all films that I go to see in the Latin Quarter, small movie theaters—kind of the remains of Henri Langlois’s Cinematheque. This is how I make my cinema. It’s something I get from my father. I’m an artist to make a living—I just do it well. I’m not alienated by it, but I’m not a specialist. And that’s why I have a small audience. I like being recognized as a filmmaker, but I don’t need to have a huge audience. It’s much more important to me to fully live my life, and be thoroughly involved with my intimates and loved ones, and my family. Life is more important. I surround myself with art to escape the ambient idiocy. But I’m less of a specialist than, for instance, Leos Carax. Because I prefer life. And I think that’s something that comes from May ’68.
RIZOV: I would like to go back to your new film for a little bit. What the couple is united by initially is their work in the editing room. At the end, when she’s the first to discover and understand that the film is based on a falsehood, she sees the footage better than he does. This seems to relate a bit to your practice of having female collaborators come in to help you write the female parts. At the same time they’re working with physical film, and he meets the other woman when he’s helping her carry cans of film. It’s a triangle united by celluloid.
GARREL: Well, even thirty years ago, if you met a woman and you were a director, she would say to you, “Make me a star.” Now, a woman will say, “Make me equal.” So the work has naturally evolved. You see, men court women naturally. Or if they like men, they court men. And by courting I mean in the medieval sense of courtship. So naturally there’s courtship in art, and I want to seduce. In the past, women wanted to be glorified in film. Now it’s different. And that changes the work of artists. Smart women today want to be equals—they won’t be upset if they’re not stars. But if they’re artists, they just want to be having their work looked at as equals, as intelligent beings. So I use that to court women. I want to meet the deepest desires of women today.
Now, the other thing is that in cinema today—cinema is young, it’s only 120 years old—most women have spoken men’s words. It’s never been an objective vision of women. So even men who are not misogynists, who love women, who see them as equals—it’s still a problem in cinema that all the words that women were speaking were coming from men. So by associating men and women in writing the films, I get to have a more dialectic type of film. More dialect in regarding the human species. It’s like an inner documentary on men and women. Cinema is not only macho, it’s industrially made by men.
So I’ve just tried to move it forward. Godard did the same thing with his second period. Which you could refer to as the Blue Period, if you’re continuing the Picasso parallel. He wrote a lot of those films with Anne-Marie Miéville. There’s one called France/tour/detour/deux/enfants, which he made for television and which I love, which he wrote with Miéville. And I think to write a film with your wife makes it intelligently gendered. The other advantage is that it’s less dangerous to write a film with your wife than to have her be the star—because you’re less likely to have someone steal her away from you. Which brings us back to the beginning of the conversation, when I was talking about Jarmusch.
[Laughter]
HYNES: And then you made an entire film about that—about whether or not a director will cast his partner as the lead in a film written about her.
GARREL: Emergency Kisses.
HUGHES: Can I ask a very practical question? In the last few films, there’s a consistent rhythm to the sequences, in that there will be a fairly static shot, like of two people sitting on a bed talking, followed by a shot of people walking down the street—there’s visual movement. I’d like to hear you talk about the design of that visual rhythm. What happens in a walking scene that can’t happen in a quiet, static scene?
GARREL: I don’t know. It’s like drawing. Those kinds of operations aren’t analyzed by the artist. I have no theory on my own film. You know, cinema is gestural; this is what it has in common with dance or with painting. You take your camera, and people, and you write something with that, that resembles life. That’s why I shoot in order. I shoot the first shot the first day, and the last shot the last day, and I edit during the shoot. I have an editor who edits as we go. So that in the evening, I see the last shot, and the next morning I continue from there. I continue from the previous image—not from what’s in the script. Once all the rehearsals are done, in a sense I could throw the story out, the actors would keep the dialogue, and we would start over.
So if you would ask me, why do you track backwards when this guy is walking down the street feeling desperate because his wife cheated on him?—it’s like painting. If I have a blue line, I look at it and I put a green line underneath it. I don’t tell myself I’m going to make a blue and green painting. I don’t theorize about that. It’s a blue line, then the green. There’s no intention before the gesture. I do it. I observe. Then I do the next thing. I observe. I do the next thing. I observe the continuity. But there’s no outside definition of what I want to get. There’s no film in my head. There’s no imaginary film I want to make. I organize reality, in the present, on the set. What I’m trying to explain to you is that it’s really gestural. I’m not reconstructing something that was constructed in my mind. I’m constructing something for the first time in reality.
HUGHES: That’s another advantage of your technique of having extensive rehearsals and then shooting a scene only once. I can’t imagine any other filmmaker that looks at the previous shot the night before, who can feel the rhythm of the movie and then make the decision the next morning based on that.
HYNES: Right, if you were considering from among fifteen takes, it would be harder to determine, tonally, what should be next.
GARREL: [in English] Ah, yes, yes. Because it’s no more clear if you make a lot of takes. That’s true. Everything is a method that you’ve invented. Every artist invents his own method. And his own method is his style. That’s why it’s so difficult to teach directing. Except for the fact of directing actors. But teaching the mise-en-scene? It’s very difficult. Because every artist is particular, every director is particular.
HYNES: But you were encouraged by Godard, your mentor, to come up with your own method. Which is quite different from other directors coming up.
GARREL: It’s also a question of misunderstanding. I thought that Godard wrote nothing at all, and that his films were entirely improvised. So through all my first films, basically from Marie for Memory to Les hautes solitudes, which is where I started to do something like preparatory work, I thought that Godard came to the set with hands in his pockets, nothing written down. In fact, I later learned that he had a notebook in which there was a story, in a few lines. He didn’t have a script but he did have a notebook, and he would give the dialogue to the actors. But since I didn’t know that, and since one doesn’t know in general how other artists work, I started doing things in my own way. So for my six first films I did absolutely no writing, I just went straight to the camera. And then at the end of the shooting I would write just a few lines of dialogue and I would give it to the actors and say, “This is for tomorrow.” This thing of misunderstanding is specific to art. It wouldn’t work with science. Art can tolerate approximation and misunderstanding. You can still have a work of art that’s based on a misunderstanding. That’s expressive.